Guidelines for Evaluating Crashworthiness of Sign Supports and Breakaway Luminaire Poles (2024)
Chapter: 4 Testing Program: Breakaway Sign Supports, PSST Posts
CHAPTER 4
Testing Program: Breakaway Sign Supports, PSST Posts
4.1 Overview
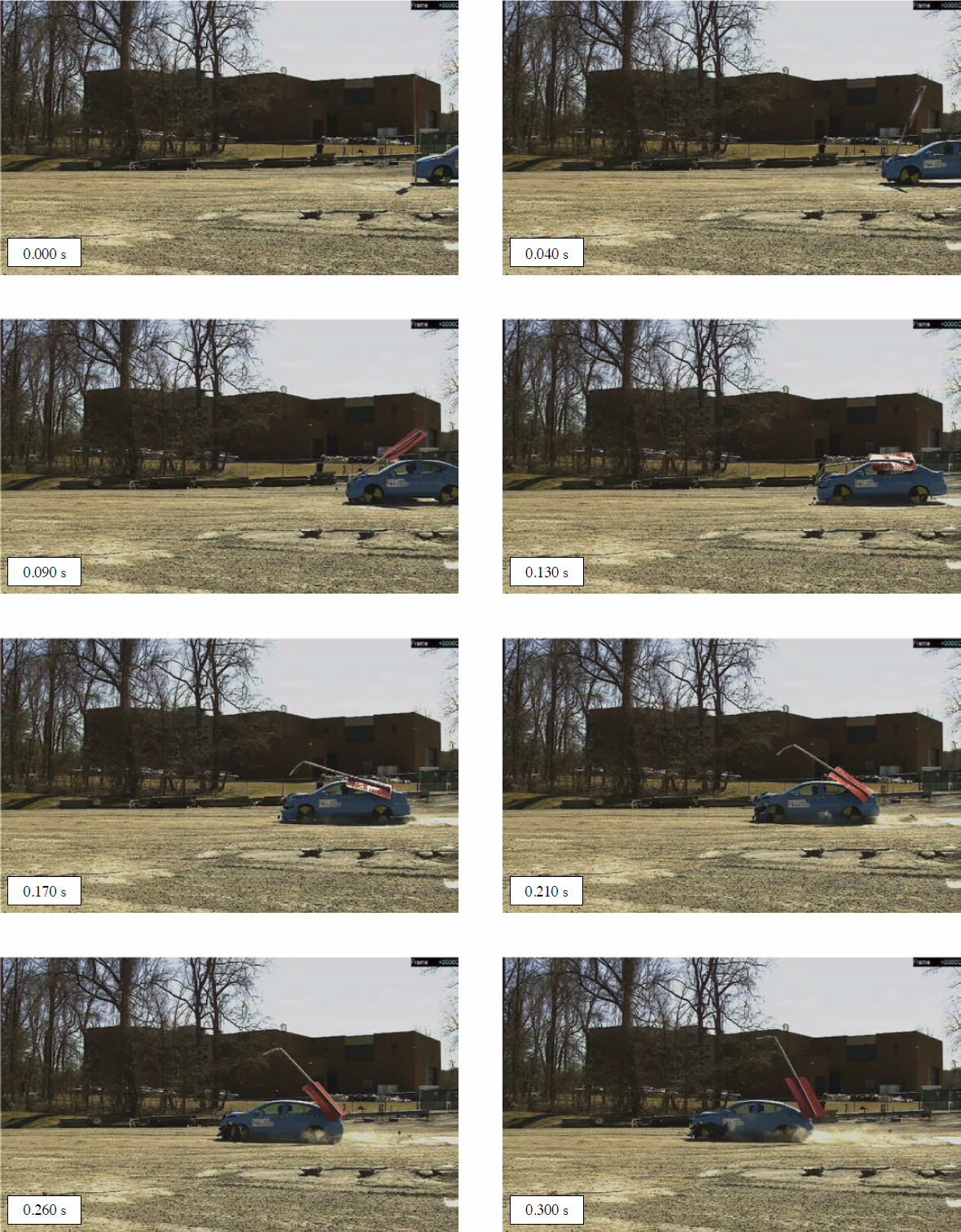
To validate the crash simulation results from the PSST analyses, five full-scale crash tests were conducted at FOIL. Detailed test reports for these tests are included in Appendices F through J. All tests were carried out following the guidelines of MASH at TL-3 impact conditions. Among these tests, three followed the MASH Test No. 3-61 impact configuration, while the other two followed the MASH Test No. 3-62 impact configuration. Figure 94 shows the pre-impact setup of the test vehicle and test article. Table 26 lists the test setup for each of the five tests. A summary of these tests is included in the following sections.
4.2 Test Requirements and Evaluation Criteria
Support structures must undergo three full-scale crash tests according to MASH guidelines. The tests for MASH TL-3 are designated as Nos. 3-60, 3-61, and 3-62 (Table 27). Test No. 3-60 involves an impact with the small car (1100C) at a speed of 19 mph, Test No. 3-61 involves an impact with a vehicle of the same size at 62 mph, and Test No. 3-62 involves an impact with the pickup test vehicle (2270P) at 62 mph. For accurate evaluation, critical impact speeds and angles are carefully selected for each test to represent the worst-case impact scenarios.
Under MASH guidelines, the evaluation criteria for “support structures” are classified into three categories: structural adequacy, occupant risk, and vehicle trajectory (AASHTO 2016). Table 28 lists the criteria for the three crash tests (criteria B, D, F, H, I, and N).
4.3 Test Article and Installation Details
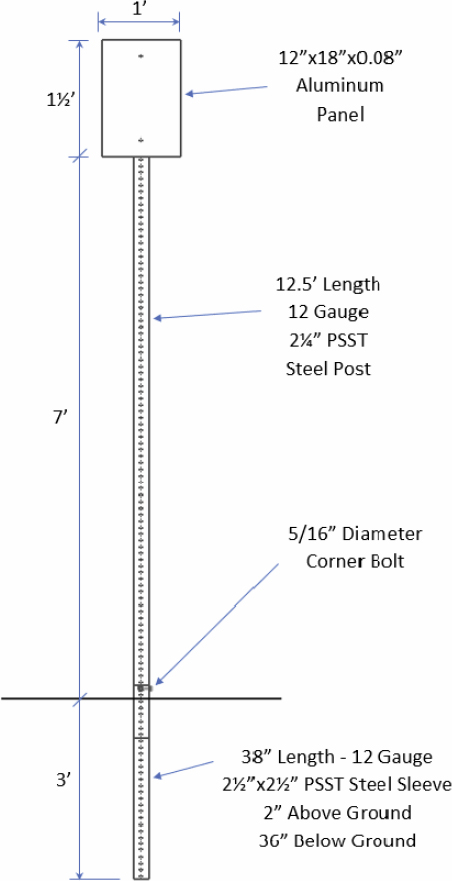
All systems tested had a 2¼-in. × 2¼-in. 12-gauge PSST post. Each post was inserted into a 2½-in. × 2½-in. 12-gauge PSST sleeve. The sleeve, which measured 38 in. in length, was embedded 36 in. below ground with 2 in. above ground. The soil surrounding the sleeve conformed to MASH standard soil. Both the post and sleeve were made of galvanized ASTM A1011 Grade 50 steel. In all tests, the sign panel was made of aluminum and mounted with its base positioned 7 ft above ground level. The panel dimensions were 1 ft × 1½ ft × 0.08 in. in Test Nos. 23004 and 23010, 4 ft × 5 ft × 0.12 in. in Test Nos. 23006 and 23008, and 3 ft × 3 ft × 0.12 in. in Test No. 23012. The panel was connected to the posts using two ⅜-in.-diameter hex head bolts with washers and nuts. The post was connected to the sleeve using a ![]() -in.-diameter bolt with washer and nut in the first test and ⅜-in. bolts in the other four tests. Figures 95 through 97 show installation sketches for the PSST systems. Table 29 summarizes the configurations of PSST systems tested.
-in.-diameter bolt with washer and nut in the first test and ⅜-in. bolts in the other four tests. Figures 95 through 97 show installation sketches for the PSST systems. Table 29 summarizes the configurations of PSST systems tested.

Table 26. Summary of PSST test configurations.
| Test Number | Date | MASH Test | Vehicle | Impact Speed | Impact Angle | Offset | Sign Panel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23004 | 02/21/23 | 3-61 | Small sedan | 62 mph | 0° | ¼W – driver side | 1 ft × 1.5 ft × 0.08 in. |
| 23006 | 03/08/23 | 3-61 | Small sedan | 62 mph | 0° | ¼W – driver side | 4 ft × 5 ft × 0.12 in. |
| 23008 | 03/22/23 | 3-62 | Pickup truck | 62 mph | 0° | 0 | 4 ft × 5 ft × 0.12 in. |
| 23010 | 04/13/23 | 3-62 | Pickup truck | 62 mph | 0° | 0 | 1 ft × 1.5 ft × 0.08 in. |
| 23012 | 04/27/23 | 3-61 | Small sedan | 62 mph | 25° | 0 | 3 ft × 3 ft × 0.12 in. |
Note: W = width of the vehicle.
Table 27. MASH test matrices for support structures (AASHTO 2016).
| Feature | Test No. | Vehicle | Impact Speeda [mph (km/h)] |
Impact Angleb (θ deg.) |
Acceptable KE Range [kip-ft (kJ)] |
Impact Point | Evaluation Criteriac |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Support Structures | 3-60 | 1100C | 19 (30) | 25 | ≤34 (41) | (c) | B, D, F, H, I, N |
| 3-61 | 1100C | 62 (100) | 25 | ≥288 (390) | (c) | B, D, F, H, I, N | |
| 3-62 | 2270P | 62 (100) | 25 | ≥594 (806) | (c) | B, D, F, H, I, N |
Notes: a See MASH Section 2.1.2 for tolerances on impact conditions; b see MASH Table 5-1; c see MASH Figure 2-5 for impact point; KE = kinetic energy.
Table 28. MASH evaluation requirements for support structures (AASHTO 2016).
| Evaluation Category | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Structural Adequacy | B. The test article should readily activate in a predictable manner by breaking away, fracturing, or yielding. |
| Occupant Risk | D. Detached elements, fragments, or other debris from the test article should not penetrate or show potential for penetrating the occupant compartment, or present an undue hazard to other traffic, pedestrians, or personnel in a work zone. Deformation of, or intrusions into, the occupant compartment should not exceed limits set forth in Section 5.3 and Appendix E of MASH. |
| F. The vehicle should remain upright during and after collision. The maximum roll and pitch angles are not to exceed 75 degrees. | |
H. OIVs should satisfy the following:
|
|
I. ORAs should satisfy:
|
|
| Vehicle Trajectory | N. Vehicle trajectory behind the test article is acceptable. |

4.4 Test Vehicles
The vehicles used in Test Nos. 23004, 23006, and 23012 conformed to the MASH criteria for the 1100C test vehicle. For Test Nos. 23008 and 23010, the vehicles adhered to the MASH 2270P test vehicle criteria. Figure 98 shows photos of typical vehicles used in these tests. Standard procedures were followed to prepare the vehicles for testing, including draining fluids and taking accurate measurements of their weight, tires, and other relevant features. The vehicles were painted blue to enhance the visibility of the impact outcomes in the multiple video cameras.
4.5 Crash Tests Outcome
Table 30 displays pre- and post-impact images from the tests. Figures 99 to 103 provide various views of the crash sequences from the five tests. The test summary sheets for each of the tests are presented in Figures 104 through 108.

In the first test, Test 23004, the ![]() -in.-diameter corner bolt connecting the post to the sleeve sheared/broke shortly after initial contact between the vehicle and the sign system. Consequently, the post separated from the sleeve, and the panel impacted the top of the driver’s side windshield, causing a tear in it. As a result, the sign system did not meet the MASH criteria for this test.
-in.-diameter corner bolt connecting the post to the sleeve sheared/broke shortly after initial contact between the vehicle and the sign system. Consequently, the post separated from the sleeve, and the panel impacted the top of the driver’s side windshield, causing a tear in it. As a result, the sign system did not meet the MASH criteria for this test.
In the second test, Test 23006, the top holes in the sleeve ruptured upon impact, leading to the post separating from the sleeve. The panel mostly impacted the roof, and the test outcome indicated that this system met all MASH criteria for this test.
During the third test, Test 23008, the post separated from the sleeve later than in the previous two tests, possibly due to the sign’s impact occurring at the center of the vehicle, which is softer than the offset point. However, this resulted in the panel impacting the windshield and causing significant deformation, exceeding the MASH critical limits.
In the fourth test, Test 23010, the post and panel primarily impacted the front of the truck and did not contact the windshield. The post ruptured at the point where it first came into contact with the vehicle’s hood (approximately 3 ft above ground level). The test outcome indicated that this system met all MASH criteria for this impact.
Table 29. Summary of sign system setups for five PSST tests.
| Test | 23004 | 23006 | 23008 | 23010 | 23012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post | 2¼-in., 12-gauge PSST | 2¼-in., 12-gauge PSST | 2¼-in., 12-gauge PSST | 2¼-in., 12-gauge PSST | 2¼-in., 12-gauge PSST |
| Post Height | 9 ft (8 in. below ground, 2 in. below top of panel) | 12½ ft (8 in. below ground, 2 in. below top of panel) | 12½ ft (8 in. below ground, 2 in. below top of panel) | 9 ft (8-in below ground, 2-in below top of panel) | 12½ ft (8 in. below ground, 2 in. below top of panel) |
| Post Material | Galvanized steel (ASTM A1011 Grade 50) | Galvanized steel (ASTM A1011 Grade 50) | Galvanized steel (ASTM A1011 Grade 50) | Galvanized steel (ASTM A1011 Grade 50) | Galvanized steel (ASTM A1011 Grade 50) |
| Sleeve Support | 2½-in., 12-gauge PSST | 2½-in., 12-gauge PSST | 2½-in., 12-gauge PSST | 2½-in., 12-gauge PSST | 2½-in., 12-gauge PSST |
| Sleeve Support Height | 38 in. (36 in. below ground, 2 in. above ground) Embedded in soil meeting MASH standards performance (compaction) | 38 in. (36 in. below ground, 2 in. above ground) Embedded in soil meeting MASH standards performance (compaction) | 38 in. (36 in. below ground, 2 in. above ground) Embedded in soil meeting MASH standards performance (compaction) | 38 in. (36 in. below ground, 2 in. above ground) Embedded in soil meeting MASH standards performance (compaction) | 38 in. (36 in. below ground, 2 in. above ground) Embedded in soil meeting MASH standards performance (compaction) |
| Sleeve Support Height | Galvanized steel (ASTM A1011 Grade 50) | Galvanized steel (ASTM A1011 Grade 50) | Galvanized steel (ASTM A1011 Grade 50) | Galvanized steel (ASTM A1011 Grade 50) | Galvanized steel (ASTM A1011 Grade 50) |
| Sign Panel Size | 1-ft width × 1.5-ft height | 4-ft width × 5-ft height | 4-ft width × 5-ft height | 1-ft width × 1.5-ft height | 3-ft width × 3-ft height |
| Sign Panel Thickness | 0.08 in. | 0.12 in. | 0.12 in. | 0.08 in. | 0.12 in. |
| Sign Panel Material | Aluminum | Aluminum | Aluminum | Aluminum | Aluminum |
| Sign Panel Mounting Height | 7 ft to base of panel | 7 ft to base of panel | 7 ft to base of panel | 7 ft to base of panel | 7 ft to base of panel |
| Post to Sleeve Connection | ⅜ bolt, Grade 5, with washers and nut | ⅜ bolt, Grade 5, with washers and nut | ⅜ bolt, Grade 5, with washers and nut | ⅜ bolt, Grade 5, with washers and nut | |
| Panel to Post Connection | Two ⅜-inch-diameter Grade 5 hex head bolts with washers and nuts | Two ⅜-inch-diameter Grade 5 hex head bolts with washers and nuts | Two ⅜-inch-diameter Grade 5 hex head bolts with washers and nuts | Two ⅜-inch-diameter Grade 5 hex head bolts with washers and nuts | Two ⅜-inch-diameter Grade 5 hex head bolts with washers and nuts |
During the last test, Test 23012, the panel impacted the windshield, causing significant deformation, although the measurement indicated it was less than the 3-in. MASH limit. A tear was noted in the windshield’s plastic inner layer, and the post sheared about 2 ft above the ground. Therefore, the sign system did not meet the MASH criteria for this impact.
Considering that each system must meet all three MASH impacts (Test Nos. 3-60, 3-61, and 3-62), none of the tested systems met the MASH requirements, consistent with the simulation results. Differences were noted between the tests and simulations, leading to further validations and calibration of the computer models.

Table 30. Evaluation summary from five PSST tests.
| Test Number | Pre-Impact | Post-Impact | MASH Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 23004 |  |
 |
Fail |
| 23006 |  |
 |
Pass |
| 23008 |  |
 |
Fail |
| 23010 |  |
 |
Pass |
| 23012 |  |
 |
Fail |


























